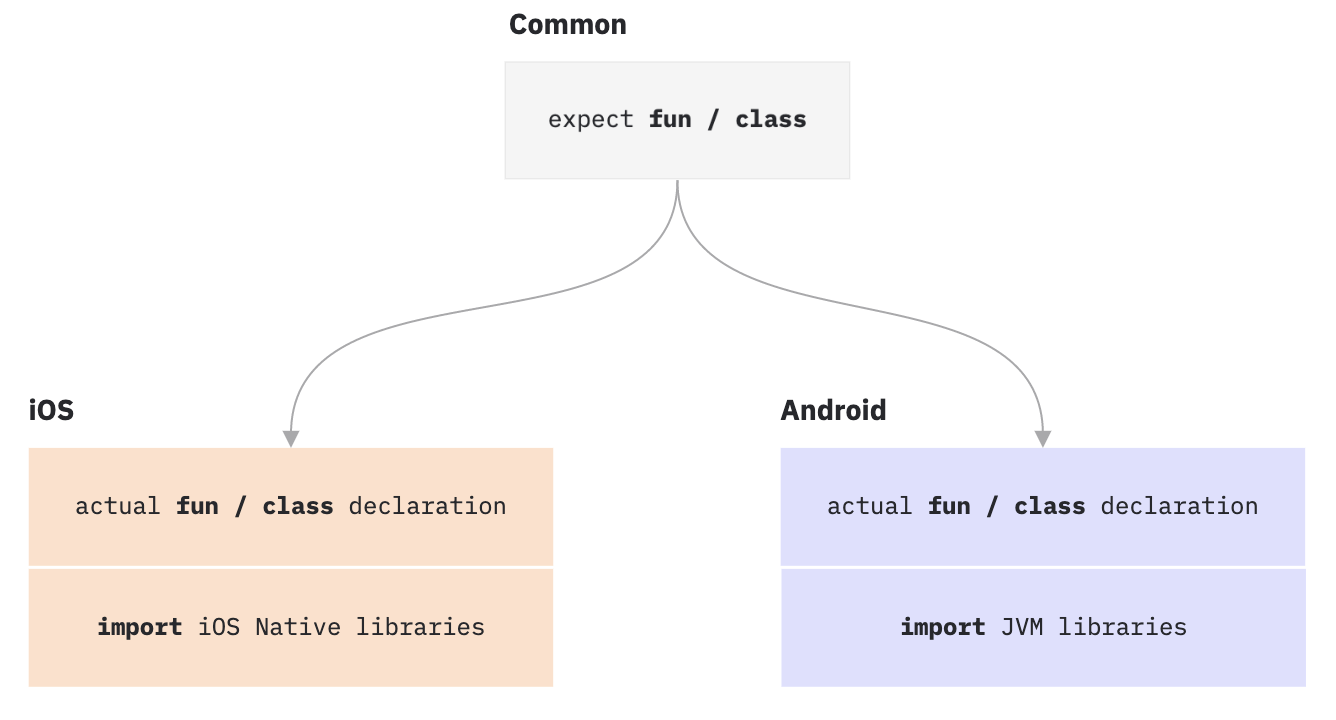
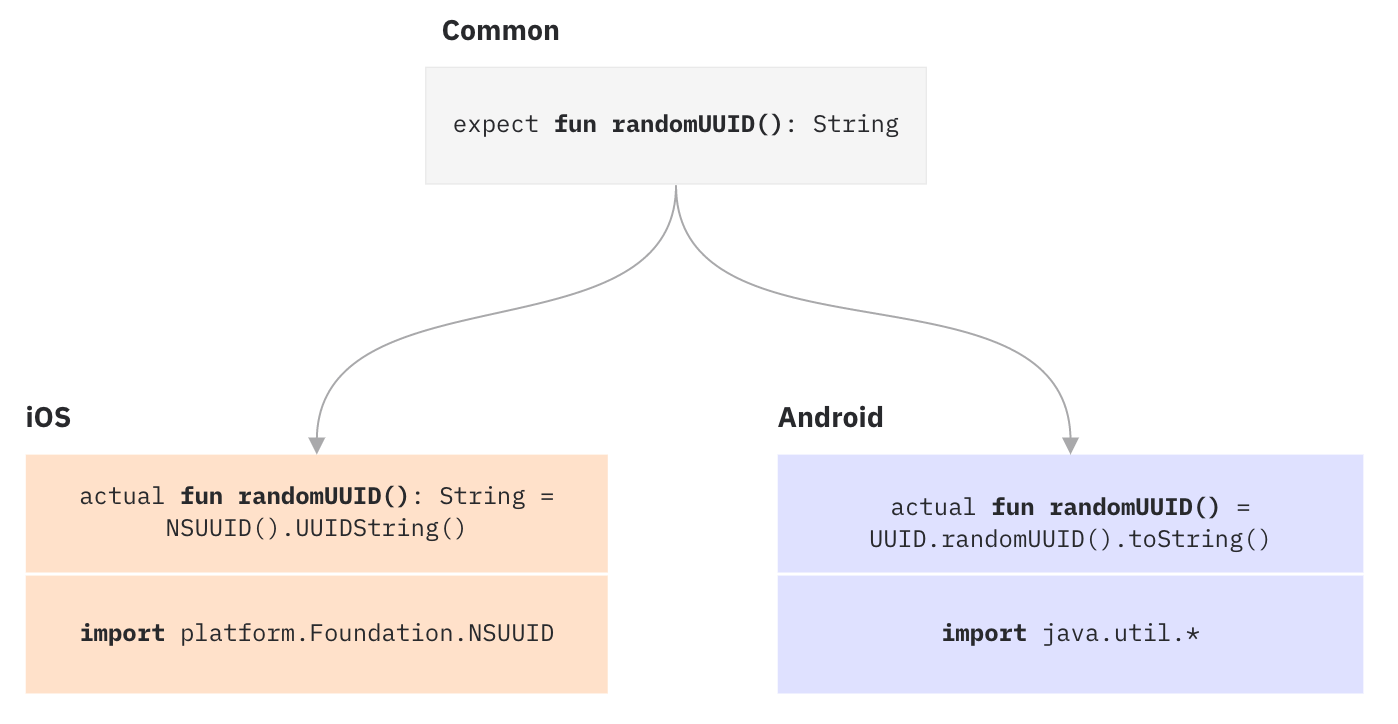
生成 UUID 假设你正在使用 Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile 开发 iOS 和 Android 应用程序, 你想要生成 Universally Unique Identifier (UUID):
为了达到这个目的, 请在共通模块中使用 expect 关键字声明预期函数 randomUUID(). 这里不要包括任何实现代码.
// 共通代码
expect fun randomUUID(): String
在每个平台相关模块中 (iOS 和 Android), 要为共通模块中预期的函数 randomUUID() 提供实际实现. 使用 actual 关键字标注实际实现.
以下示例演示这个函数在 Android 和 iOS 上的实现. 平台相关代码使用 actual 关键字加上预期函数的名称.
// Android 平台代码
import java.util.*
actual fun randomUUID() = UUID.randomUUID().toString()
// iOS 平台代码
import platform.Foundation.NSUUID
actual fun randomUUID(): String = NSUUID().UUIDString()
实现一个 log 框架 另一个例子, 在一个极简化的 log 框架中, 演示如何编写共通代码, 并实现共通代码与平台逻辑之间的交互, 这个例子中的平台是 JS 和 JVM:
// 共通代码
enum class LogLevel {
DEBUG, WARN, ERROR
}
internal expect fun writeLogMessage(message: String, logLevel: LogLevel)
fun logDebug(message: String) = writeLogMessage(message, LogLevel.DEBUG)
fun logWarn(message: String) = writeLogMessage(message, LogLevel.WARN)
fun logError(message: String) = writeLogMessage(message, LogLevel.ERROR)
// JVM 平台代码
internal actual fun writeLogMessage(message: String, logLevel: LogLevel) {
println("[$logLevel]: $message")
}
对于 JavaScript, 可以使用的 API 完全不同, actual 声明大致如下.
// JS 平台代码
internal actual fun writeLogMessage(message: String, logLevel: LogLevel) {
when (logLevel) {
LogLevel.DEBUG -> console.log(message)
LogLevel.WARN -> console.warn(message)
LogLevel.ERROR -> console.error(message)
}
}
通过 WebSocket 发送和接收消息 假设你在使用 Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile 为 iOS 和 Android 开发一个聊天平台. 我们来看看如何实现通过 WebSocket 发送和接收消息的功能.
为了达到这个目的, 请定义一个共通逻辑, 你不需要在所有平台模块中重复实现这段逻辑 – 只需要在共通模块中实现一次. 但是, WebSocket 类的实际实现在各个平台不同. 所以你应该对这个类使用 expect/actual 声明.
在共通模块中, 使用 expect 关键字声明预期类 PlatformSocket(). 不要包含任何实现代码.
// 共通代码
internal expect class PlatformSocket(
url: String
) {
fun openSocket(listener: PlatformSocketListener)
fun closeSocket(code: Int, reason: String)
fun sendMessage(msg: String)
}
interface PlatformSocketListener {
fun onOpen()
fun onFailure(t: Throwable)
fun onMessage(msg: String)
fun onClosing(code: Int, reason: String)
fun onClosed(code: Int, reason: String)
}
在每个平台相关模块中 (iOS 和 Android), 要为共通模块中预期的 PlatformSocket() 类提供实际实现. 使用 actual 关键字标注实际实现.
以下示例演示这个类在 Android 和 iOS 上的实现.
// Android 平台代码
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient
import okhttp3.Request
import okhttp3.Response
import okhttp3.WebSocket
internal actual class PlatformSocket actual constructor(url: String) {
private val socketEndpoint = url
private var webSocket: WebSocket? = null
actual fun openSocket(listener: PlatformSocketListener) {
val socketRequest = Request.Builder().url(socketEndpoint).build()
val webClient = OkHttpClient().newBuilder().build()
webSocket = webClient.newWebSocket(
socketRequest,
object : okhttp3.WebSocketListener() {
override fun onOpen(webSocket: WebSocket, response: Response) = listener.onOpen()
override fun onFailure(webSocket: WebSocket, t: Throwable, response: Response?) = listener.onFailure(t)
override fun onMessage(webSocket: WebSocket, text: String) = listener.onMessage(text)
override fun onClosing(webSocket: WebSocket, code: Int, reason: String) = listener.onClosing(code, reason)
override fun onClosed(webSocket: WebSocket, code: Int, reason: String) = listener.onClosed(code, reason)
}
)
}
actual fun closeSocket(code: Int, reason: String) {
webSocket?.close(code, reason)
webSocket = null
}
actual fun sendMessage(msg: String) {
webSocket?.send(msg)
}
}
Android 实现使用第 3 方库 OkHttp . 请向共用模块中的 build.gradle(.kts) 添加对应的依赖项:
sourceSets {
val androidMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:$okhttp_version")
}
}
}
commonMain {
dependencies {
implementation "com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:$okhttp_version"
}
}
iOS 实现使用 Apple 标准 SDK 的 NSURLSession, 不需要额外的依赖项.
// iOS 平台代码
import platform.Foundation.*
import platform.darwin.NSObject
internal actual class PlatformSocket actual constructor(url: String) {
private val socketEndpoint = NSURL.URLWithString(url)!!
private var webSocket: NSURLSessionWebSocketTask? = null
actual fun openSocket(listener: PlatformSocketListener) {
val urlSession = NSURLSession.sessionWithConfiguration(
configuration = NSURLSessionConfiguration.defaultSessionConfiguration(),
delegate = object : NSObject(), NSURLSessionWebSocketDelegateProtocol {
override fun URLSession(
session: NSURLSession,
webSocketTask: NSURLSessionWebSocketTask,
didOpenWithProtocol: String?
) {
listener.onOpen()
}
override fun URLSession(
session: NSURLSession,
webSocketTask: NSURLSessionWebSocketTask,
didCloseWithCode: NSURLSessionWebSocketCloseCode,
reason: NSData?
) {
listener.onClosed(didCloseWithCode.toInt(), reason.toString())
}
},
delegateQueue = NSOperationQueue.currentQueue()
)
webSocket = urlSession.webSocketTaskWithURL(socketEndpoint)
listenMessages(listener)
webSocket?.resume()
}
private fun listenMessages(listener: PlatformSocketListener) {
webSocket?.receiveMessageWithCompletionHandler { message, nsError ->
when {
nsError != null -> {
listener.onFailure(Throwable(nsError.description))
}
message != null -> {
message.string?.let { listener.onMessage(it) }
}
}
listenMessages(listener)
}
}
actual fun closeSocket(code: Int, reason: String) {
webSocket?.cancelWithCloseCode(code.toLong(), null)
webSocket = null
}
actual fun sendMessage(msg: String) {
val message = NSURLSessionWebSocketMessage(msg)
webSocket?.sendMessage(message) { err ->
err?.let { println("send $msg error: $it") }
}
}
}
下面是共通模块中的共通逻辑, 它使用平台相关的 PlatformSocket() 类.
// 共通代码
class AppSocket(url: String) {
private val ws = PlatformSocket(url)
var socketError: Throwable? = null
private set
var currentState: State = State.CLOSED
private set(value) {
field = value
stateListener?.invoke(value)
}
var stateListener: ((State) -> Unit)? = null
set(value) {
field = value
value?.invoke(currentState)
}
var messageListener: ((msg: String) -> Unit)? = null
fun connect() {
if (currentState != State.CLOSED) {
throw IllegalStateException("The socket is available.")
}
socketError = null
currentState = State.CONNECTING
ws.openSocket(socketListener)
}
fun disconnect() {
if (currentState != State.CLOSED) {
currentState = State.CLOSING
ws.closeSocket(1000, "The user has closed the connection.")
}
}
fun send(msg: String) {
if (currentState != State.CONNECTED) throw IllegalStateException("The connection is lost.")
ws.sendMessage(msg)
}
private val socketListener = object : PlatformSocketListener {
override fun onOpen() {
currentState = State.CONNECTED
}
override fun onFailure(t: Throwable) {
socketError = t
currentState = State.CLOSED
}
override fun onMessage(msg: String) {
messageListener?.invoke(msg)
}
override fun onClosing(code: Int, reason: String) {
currentState = State.CLOSING
}
override fun onClosed(code: Int, reason: String) {
currentState = State.CLOSED
}
}
enum class State {
CONNECTING,
CONNECTED,
CLOSING,
CLOSED
}
}