Kotlin Notebook 支持的输出格式
Kotlin Notebook 支持很多种输出类型, 包括文本, HTML, 和图片. 通过使用外部库, 你可以选择更多的输出类型, 并使用图表, 电子表格, 等等形式, 可视化你的数据.
每个输出都是一个 JSON 对象, 将 Jupiter MIME 类型 对应到一些数据. 通过这个对应 map, Kotlin Notebook 从支持的 MIME 类型中选择最高优先级的类型, 并通过以下方式展现它:
Text 使用
text/plainMIME 类型.BufferedImage 类 使用
image/pngMIME 类型, 对应到一个 Base64 字符串.Kotlin DataFrame 表格 和 Kandy 绘图 使用它们自己的内部 MIME 类型, 通过静态的 HTML 或图片实现. 通过这种方式, 你可以在 GitHub 上显示它们.
你可以手动设置这个对应关系, 例如, 要使用 Markdown 作为 cell 的输出:
要显示任何类型的输出, 请使用 DISPLAY() 函数. 它还能够使用多种输出的组合:
文本
纯文本(Plain Text)
最简单的输出类型是纯文本. 它可以用于打印输出文字, 变量值, 或者你的代码中的任何文本输出:

如果一个 cell 的结果无法 展现 并显示为任何一种输出类型, 那么它会被使用
toString()函数打印输出为纯文本.如果你的代码包含错误, Kotlin Notebook 会显示一个错误信息, 和一个错误追溯(traceback), 提供调试信息.
富文本(Rich Text)
请选择 Markdown 类型的 cell 来使用 富文本. 通过这种方式, 你可以使用 Markdown 和 HTML 标记格式化内容, 使用列表, 表格, 字体, 代码块, 等等. HTML 可以包含 CSS 样式 和 JavaScript.
HTML
Kotlin Notebook 能够直接展现 HTML, 执行脚本, 甚至还能嵌入 Web 站点:

图片
使用 Kotlin Notebook, 你可以显示图片, 图片可以来自文件, 生成的图形, 或者任何其他视觉媒体. 可以显示各种格式的静态图片, 例如 .png, jpeg, 和 .svg.
缓冲的图片
默认情况下, 你可以使用 BufferedImage 类显示图片:
从外部加载的图片
通过使用 lib-ext 库, 你可以扩展标准的 Jupyter 的功能, 显示从网络加载的图片:

内嵌的图片
从网络加载图片的一个缺点是, 如果链接错误, 或者失去网络连接, 图片就会消失. 要解决这个问题, 请使用内嵌的图片, 例如:
数学公式和方程式
你可以使用 LaTeX 格式展现数学公式和方程式, 这是一种在学术界广泛使用的排版系统:
添加
lib-ext库, 它会向你的 Notebook 扩展 Jupyter Kernel 的功能:%use lib-ext(0.11.0-398)在新的 cell 中, 运行你的公式:
LATEX("c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2 a b \\cos\\alpha")
数据帧(Data Frame)
使用 Kotlin Notebook, 你可以通过数据帧可视化结构化的数据:
向你的 Notebook 添加 Kotlin DataFrame 库:
%use dataframe在新的 cell 中, 创建数据帧, 并运行它:
val months = listOf( "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December" ) // 各种产品/各个月份的销售数据: val salesLaptop = listOf(120, 130, 150, 180, 200, 220, 240, 230, 210, 190, 160, 140) val salesSmartphone = listOf(90, 100, 110, 130, 150, 170, 190, 180, 160, 140, 120, 100) val salesTablet = listOf(60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 110, 100, 90, 80, 70) // 一个数据帧, 包含 Month, Sales, 和 Product 的列 val dfSales = dataFrameOf( "Month" to months + months + months, "Sales" to salesLaptop + salesSmartphone + salesTablet, "Product" to List(12) { "Laptop" } + List(12) { "Smartphone" } + List(12) { "Tablet" }, )这个数据帧使用
dataFrameOf()函数, 包含几种产品 (笔记本电脑, 手机, 以及平板电脑) 在 12 个月内的销售数量.浏览你的数据帧中的数据, 例如, 查找销售数量最高的产品和月份:
dfSales.maxBy("Sales")
你也可以将你的数据帧导出为 CSV 文件:
// 将你的数据导出为 CSV 格式 dfSales.writeCSV("sales-stats.csv")
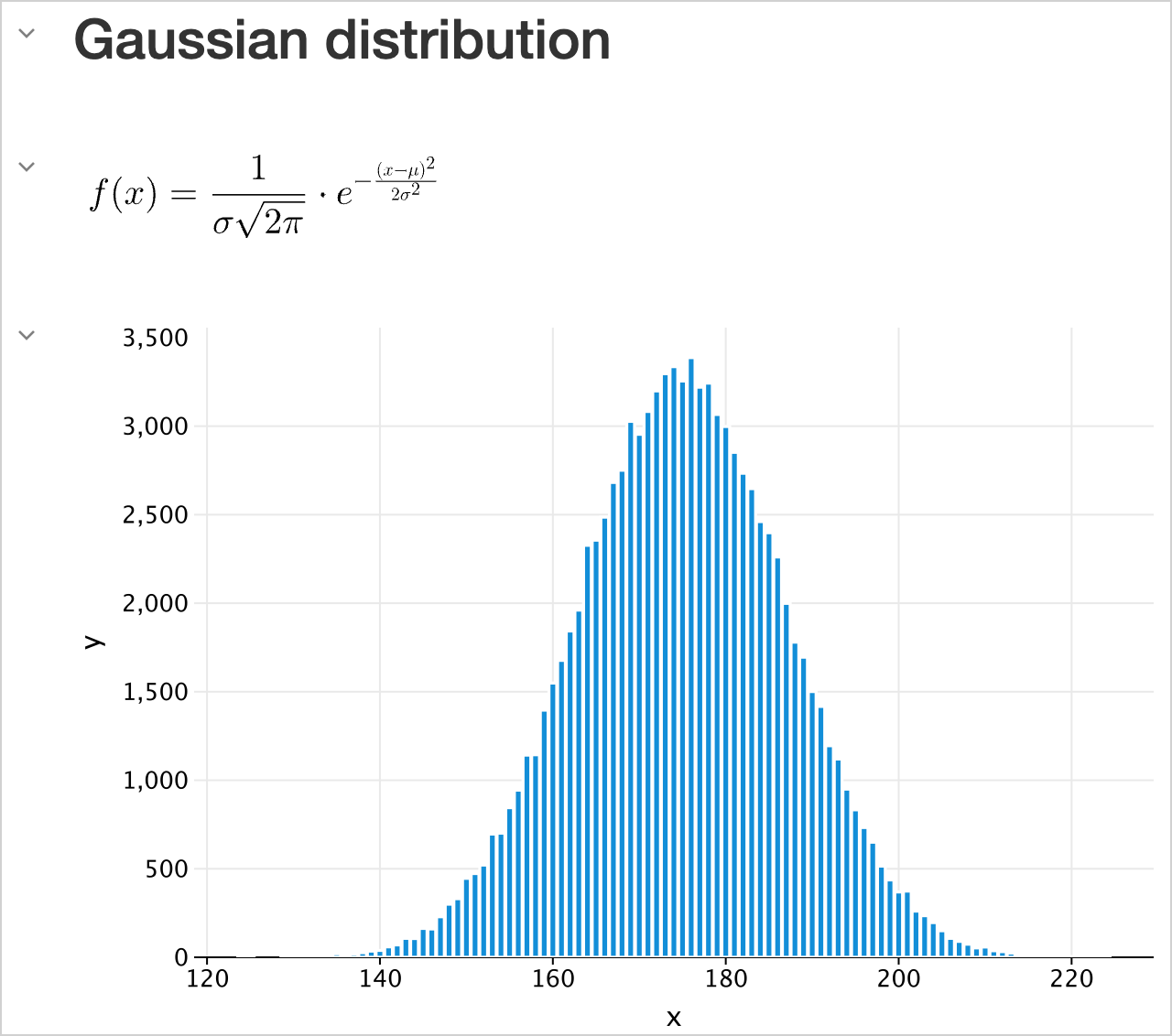
图表
你可以在你的 Kotlin Notebook 中直接创建各种图表, 来可视化你的数据:
向你的 Notebook添加 Kandy 绘图库:
%use kandy在新的 cell 中使用同一个数据帧, 运行
plot()函数:val salesPlot = dfSales.groupBy { Product }.plot { bars { // 访问数据帧的列, 用于 X 轴和 Y 轴 x(Month) y(Sales) // 访问数据帧的列, 用于分组, 并为这些分组设置颜色 fillColor(Product) { scale = categorical( "Laptop" to Color.PURPLE, "Smartphone" to Color.ORANGE, "Tablet" to Color.GREEN ) legend.name = "Product types" } } // 定制图表的外观 layout.size = 1000 to 450 layout.title = "Yearly Gadget Sales Results" } salesPlot
你也可以将你的图表导出为
.png,jpeg,.html, 或.svg格式:// 为图表文件指定输出格式: salesPlot.save("sales-chart.svg")